Description
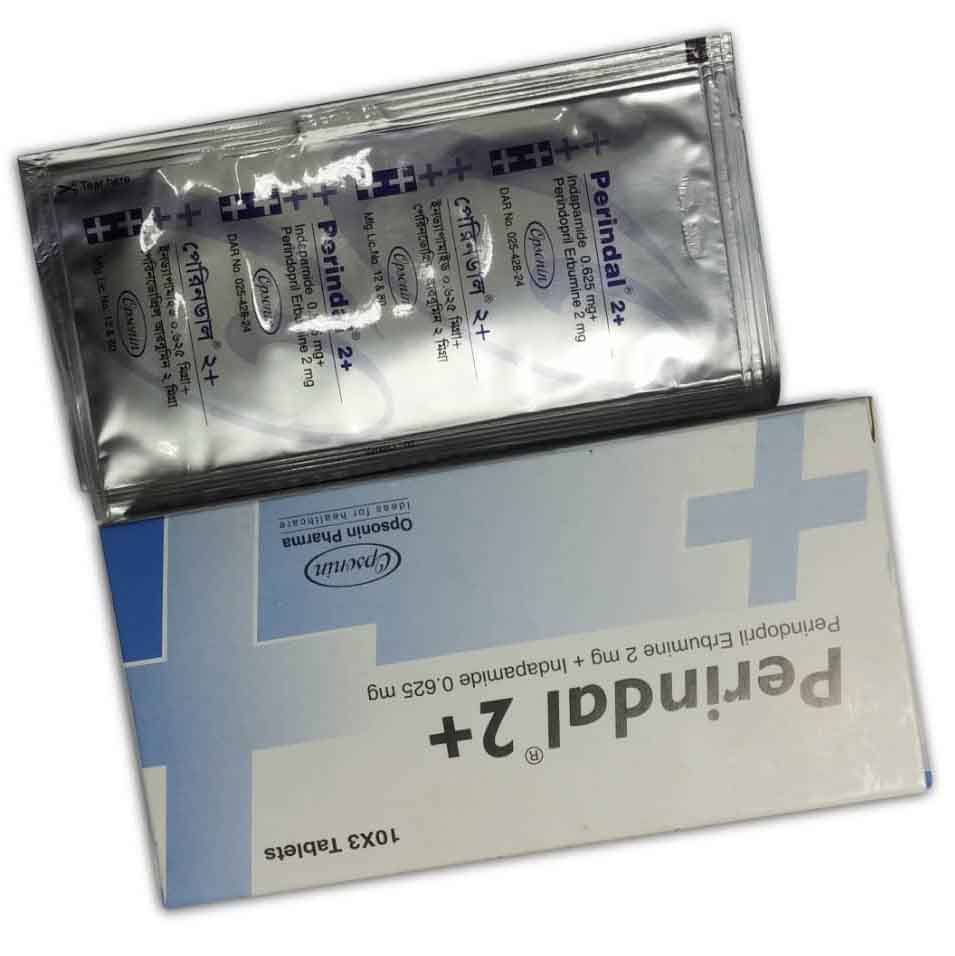
Brand Name: Perindal 2+®
Generic Name : Perindopril Erbumine 2mg/ Indapamide 0.625mg.
How does this medication work? What will it do for me?
This combination product contains 2 medications: perindopril and indapamide. It is used to treat adults with mild to moderate high blood pressure.
Perindopril belongs to the class of medications called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors . It works by relaxing blood vessels and helping the heart to pump blood that carries oxygen to the different parts of the body more efficiently.
Indapamide belongs to the class of medications called diuretics or “water pills,” which help control blood pressure by getting rid of excess salt and water.
This combination medication is prescribed when your doctor feels it is appropriate for you to be taking both medications.
This medication may be available under multiple brand names and/or in several different forms. Any specific brand name of this medication may not be available in all of the forms or approved for all of the conditions discussed here. As well, some forms of this medication may not be used for all of the conditions discussed here.
Your doctor may have suggested this medication for conditions other than those listed in these drug information articles. If you have not discussed this with your doctor or are not sure why you are taking this medication, speak to your doctor. Do not stop taking this medication without consulting your doctor.
Do not give this medication to anyone else, even if they have the same symptoms as you do. It can be harmful for people to take this medication if their doctor has not prescribed it.
How should I use this medication?
This combination medication is used to make dosing more convenient for people who need to take both of these medications (perindopril and indapamide). The dose of the combination medication depends on the doses of the individual medications the person needs.
The usual recommended dose of this medication is one tablet taken once a day, preferably in the morning before a meal.
Many things can affect the dose of medication that a person needs, such as body weight, other medical conditions, and other medications. If your doctor has recommended a dose different from the ones listed here, do not change the way that you are taking the medication without consulting your doctor.
It is important that this medication be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor. If you miss a dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one. If you are not sure what to do after missing a dose, contact your doctor or pharmacist for advice.
Store this medication at room temperature and keep it out of the reach of children.
Do not dispose of medications in wastewater (e.g. down the sink or in the toilet) or in household garbage. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medications that are no longer needed or have expired.
Who should NOT take this medication?
Do not use perindopril – indapamide if you:
Are allergic to perindopril, indapamide, or any ingredients of the medication
Are allergic to sulfa (sulfonamide) medications (e.g., sulfamethoxazole)
Are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant
Are breast-feeding
Have decreased kidney function or are unable to pass urine
Have untreated high or low potassium
Have had angioedema (a serious allergic reaction that causes the area around the throat and tongue to swell) after taking any ACE inhibitors (e.g., captopril, ramipril)
Have diabetes or kidney disease and are taking aliskiren
Have galactose intolerance (a rare hereditary disease) or lactose intolerance
Have hereditary angioedema (a serious allergic reaction which causes swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, face, lips, tongue, or throat) or have angioedema with no known cause
Have severely decreased liver function or have hepatic encephalopathy
Are taking other medications that affect heart rhythm
This medication should not be given to anyone who is in a coma due to reduced liver function.
What side effects are possible with this medication?
Many medications can cause side effects. A side effect is an unwanted response to a medication when it is taken in normal doses. Side effects can be mild or severe, temporary or permanent.
The side effects listed below are not experienced by everyone who takes this medication. If you are concerned about side effects, discuss the risks and benefits of this medication with your doctor.
The following side effects have been reported by at least 1% of people taking this medication. Many of these side effects can be managed, and some may go away on their own over time.
Contact your doctor if you experience these side effects and they are severe or bothersome. Your pharmacist may be able to advise you on managing side effects.
abdominal pain, cold-like symptoms, constipation, cough (dry, persistent), diarrhea, dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, headache, heartburn, loss of appetite, nausea, pins and needles sensation, spinning sensation, sweating, taste changes (e.g., metallic taste), tiredness, vomiting, weakness
Although most of the side effects listed below don’t happen very often, they could lead to serious problems if you do not check seek medical attention. Check with your doctor as soon as possible if any of the following side effects occur:
Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting (signs of low blood pressure)
Fast or irregular heartbeat
Joint pain (e.g., toe pain may be a sign of gout)
Muscle cramps or unexplained muscle pain
Signs of anemia (low red blood cells; e.g., dizziness, pale skin, unusual tiredness or weakness, shortness of breath)
Signs of bleeding (e.g., unusual nosebleeds, bruising, blood in urine, coughing blood, bleeding gums, cuts that don’t stop bleeding)
Signs of infection (symptoms may include fever or chills, severe diarrhea, shortness of breath, prolonged dizziness, headache, stiff neck, weight loss, or listlessness)
Signs of high blood calcium levels (e.g., loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation or stomach pain)
Signs of kidney problems (e.g., decreased urination, nausea, vomiting, swelling of legs, hands, fatigue)
Signs of liver problems (e.g., abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting, itching of skin, yellow eyes or skin)
Signs of too much or too little potassium in the body (e.g., dry mouth; increased thirst; irregular heartbeat; mood or mental changes; muscle cramps or pain; numbness or tingling in hands, feet, or lips; weak pulse; weakness or heaviness of legs)
Skin rash, with or without itching, fever, or joint pain
Stomach pain (severe) with nausea and vomiting
Swelling of hands, ankles or feet
Symptoms of high blood sugar (e.g., frequent urination, increased thirst, excessive eating, unexplained weight loss, poor wound healing, infections, fruity breath odour)
Vision changes
Stop taking the medication and seek immediate medical attention if any of the following occur:
Chest pain
Difficulty breathing
Formation of clusters of blisters over the skin
Signs of pancreatitis (e.g., abdominal pain on the upper left side, back pain, nausea, fever, chills, rapid heartbeat, swollen abdomen)
Symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including angioedema (e.g., hives; swelling of the face, mouth, hands, or feet; and difficulty breathing)
Severe skin rash, including skin blistering and peeling (possibly with headache, fever, coughing, or aching before the rash begins)
Symptoms of increased pressure in the eyes (e.g., decreased or blurred vision, eye pain, red eye, swelling of the eye)
Some people may experience side effects other than those listed. Check with your doctor if you notice any symptom that worries you while you are taking this medication.
Are there any other precautions or warnings for this medication?
Before you begin using a medication, be sure to inform your doctor of any medical conditions or allergies you may have, any medications you are taking, whether you are pregnant or breast-feeding, and any other significant facts about your health. These factors may affect how you should use this medication.
Abnormal heart rhythms: This medication can cause abnormal heart rhythms. Certain medications (e.g., sotalol, quinidine, thioridazine, chlorpromazine, droperidol, pimozide, moxifloxacin, mefloquine, pentamidine, arsenic trioxide, dolasetron mesylate, tacrolimus) can increase the risk of a type of abnormal heart rhythm called torsades de pointes and should be used with caution with indapamide.
If you are taking medication for abnormal heart rhythms, discuss with your doctor how this medication may affect your medical condition, how your medical condition may affect the dosing and effectiveness of this medication, and whether any special monitoring is needed.
Allergic reaction: This medication may cause a serious allergic reaction called angioedema, which may be fatal if not treated promptly. If you have difficulty breathing, notice hives or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, stop taking this medication and get emergency.